Class 36: Introduction to Deployment & Cloud Platforms
You've learned to build both frontend and backend applications. But how do you make your application accessible to users around the world? This is where deployment comes in. Today, we'll introduce the concepts of web application deployment and explore the world of Cloud Computing and various deployment platforms.
Understanding Web Application Deployment
-
What is deployment?
Deployment is the process of making your web application available to users over the internet. It involves taking your code, setting up servers, configuring databases, and making sure everything runs smoothly so that users can access your application via a web browser.
-
Deployment stages:
A typical software development lifecycle involves several environments:
- Development: Your local machine, where you write and test code.
- Testing/QA (Quality Assurance): An environment where automated and manual tests are run to ensure quality.
- Staging/Pre-production: A replica of the production environment used for final testing before release.
- Production: The live environment where your application is accessible to end-users.
-
Key considerations for deployment:
- Scalability: Can your application handle increasing user traffic and data?
- Reliability: Is your application available and performing consistently? What happens if a server fails?
- Security: Is your application and user data protected from threats?
- Cost: How much will it cost to run and maintain your application?
Introduction to Cloud Computing
Cloud computing is the on-demand delivery of IT resources over the internet with pay-as-you-go pricing. Instead of owning and maintaining your own computing infrastructure, you can access services like servers, storage, databases, networking, analytics, and intelligence from a cloud provider.
-
Benefits:
- Cost-effectiveness: Pay only for what you use, no upfront capital expenditure.
- Global scale: Deploy applications globally in minutes.
- Performance: Access to high-performance hardware and optimized networks.
- Security: Cloud providers invest heavily in security measures and compliance.
- Agility: Rapidly provision and de-provision resources as needed.
-
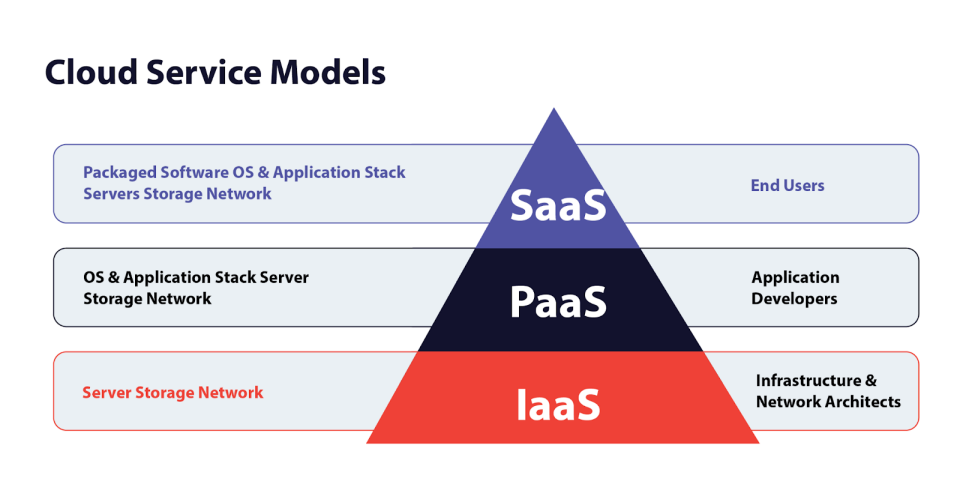
Service Models:
Cloud services are typically categorized into three main types:
-
IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service):
Provides virtualized computing resources over the
internet. You manage the operating system,
applications, and data.
Examples: Amazon EC2 (Virtual Servers), Google Compute Engine, Microsoft Azure Virtual Machines. -
PaaS (Platform as a Service):
Provides a complete environment for developing,
running, and managing applications without the
complexity of building and maintaining the
infrastructure. You focus on your code.
Examples: Heroku, AWS Elastic Beanstalk, Google App Engine, Netlify, Vercel. -
SaaS (Software as a Service):
Ready-to-use software applications delivered over
the internet, managed by a third-party vendor. You
just use the software.
Examples: Gmail, Salesforce, Dropbox.
-
IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service):
Provides virtualized computing resources over the
internet. You manage the operating system,
applications, and data.
Major Cloud Providers (High-Level Overview)
-
Amazon Web Services (AWS):
The dominant cloud provider, offering a vast and deep array of services (compute, storage, databases, machine learning, etc.). Can be complex to navigate initially.
-
Google Cloud Platform (GCP):
Known for its strengths in AI/ML, data analytics, and container orchestration (Kubernetes). Often considered developer-friendly.
-
Microsoft Azure:
Strong integration with Microsoft enterprise products and hybrid cloud solutions.
-
Other players:
DigitalOcean (simpler VPS hosting), Vercel (frontend deployment, serverless functions), Netlify (static site hosting, serverless functions).
Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) for Web Apps
PaaS solutions are excellent for web developers because they abstract away much of the underlying infrastructure, allowing you to focus on writing code.
-
Benefits of PaaS:
- Abstracts infrastructure management (servers, OS, networking).
- Focus on code deployment, not server configuration.
- Often includes automatic scaling.
- Simplified deployment pipelines (e.g., Git integration).
-
Heroku:
A popular PaaS, especially for full-stack applications. It uses "Dynos" (containers) and "Buildpacks" to automatically detect and run your application.
-
Render:
A unified cloud platform to build and run all your apps and websites with free TLS certificates, a global CDN, DDoS protection, private networks, and auto deploys from Git. A strong Heroku competitor.
-
Netlify / Vercel:
Specialized PaaS platforms primarily for static sites (your React/Vue builds) and serverless functions. They offer incredibly simple deployment directly from Git repositories, continuous deployment, and global CDNs.
Deploying a Simple Static Frontend Application
Let's walk through the general steps to deploy a static frontend application (like a React app) using Netlify or Vercel.
Prerequisites:
- A React application (or any static HTML/CSS/JS project).
- Your project committed to a GitHub repository.
Steps (using Netlify as an example):
-
Build your application:
For a React app created with Vite, this generates the optimized static files in a
distfolder.cd my-react-app npm run build -
Sign up for Netlify (or Vercel):
Go to netlify.com and sign up using your GitHub account.
-
Connect to GitHub repository:
In Netlify, click "Add new site" -> "Import an existing project" -> "Deploy with GitHub". Authorize Netlify to access your repositories.
- Select your repository: Choose the GitHub repository containing your React project.
-
Configure build settings:
Netlify will usually auto-detect your framework (e.g., React with Vite).
-
Build command:
npm run build -
Publish directory:
dist(orbuildfor Create React App)
-
Build command:
- Deploy site: Click "Deploy site". Netlify will clone your repo, run the build command, and deploy the contents of your publish directory to a global CDN.
-
Automatic builds and deployments:
Once set up, Netlify automatically detects new commits to your connected Git branch (e.g.,
main) and triggers a new build and deployment. This is Continuous Deployment (CD) for your frontend. - Custom domains: You can easily configure a custom domain for your deployed application.
Environment Variables for Production
When deploying your application, you must handle sensitive data (like API keys, database credentials, JWT secrets) securely. Never commit these directly to your Git repository.
-
Managing securely in production:
Cloud platforms provide mechanisms to set environment variables directly in their configuration. These variables are injected into your application's runtime environment.
- Heroku: Use Config Vars in your app settings.
- Netlify/Vercel: Use Environment Variables in site settings.
- AWS/GCP/Azure: Use their respective environment variable management systems (e.g., Lambda environment variables, ECS task definitions).
-
Your Node.js application will then access these using
process.env.YOUR_VARIABLE_NAME, just like with your local.envfile.
This class introduced you to the crucial step of deployment and the power of cloud platforms. While we focused on static frontend deployment, the principles extend to backend applications as well. In the next class, we'll explore Docker and containerization, which are fundamental technologies for modern deployments.
