Class 34: Advanced Backend Topics - Error Handling & Logging
Building robust backend applications requires more than just implementing features. It demands careful consideration of how errors are handled and how application behavior is logged. Today, we'll dive into advanced error handling patterns in Express.js and introduce effective logging strategies. We'll also briefly discuss API documentation and environment configuration.
Centralized Error Handling in Express
In a production application, you don't want to scatter
try...catch blocks everywhere or send inconsistent
error responses. Centralized error handling provides a single,
consistent way to manage errors across your API.
-
Why centralized error handling?
-
Avoids repetitive
try...catchblocks. - Ensures consistent error response format (e.g., JSON).
- Separates error logic from business logic.
- Provides a single point for logging errors.
-
Avoids repetitive
-
The Express error handling middleware:
Express recognizes a middleware function as an error handler if it has four arguments:
(err, req, res, next). These functions must be defined after all otherapp.use()and route calls.
Handling 404 Not Found errors:
Any request that doesn't match a defined route will fall through to this middleware.
// server.js (main file, place this AFTER all your routes)
// Catch-all for 404 Not Found
app.use((req, res, next) => {
res.status(404).json({
success: false,
message: `The resource at ${req.originalUrl} was not found.`
});
});
Creating Custom Error Classes:
To provide more specific error types and messages, you can create custom error classes that extend Node.js's built-in `Error` class.
// utils/ApiError.js
class ApiError extends Error {
constructor(message, statusCode, errors = []) {
super(message);
this.statusCode = statusCode;
this.status = `${statusCode}`.startsWith('4') ? 'fail' : 'error';
this.isOperational = true; // Operational errors are expected (e.g., validation)
this.errors = errors; // Array for validation errors
Error.captureStackTrace(this, this.constructor); // Captures stack trace
}
}
module.exports = ApiError;
Centralized Error Handling Middleware:
This middleware will catch all errors passed to
next(err)
and send a consistent JSON response.
// middleware/errorHandler.js
const ApiError = require('../utils/ApiError');
const errorHandler = (err, req, res, next) => {
let error = { ...err }; // Copy the error object
error.message = err.message;
// Log the error for debugging (you'll replace this with a logger later)
console.error(err.stack);
// Mongoose Bad ObjectId
if (err.name === 'CastError') {
const message = `Resource not found with id of ${err.value}`;
error = new ApiError(message, 404);
}
// Mongoose Duplicate Key (e.g., unique email)
if (err.code === 11000) {
const message = `Duplicate field value entered: ${Object.keys(err.keyValue)}`;
error = new ApiError(message, 400);
}
// Mongoose Validation Error
if (err.name === 'ValidationError') {
const messages = Object.values(err.errors).map(val => val.message);
error = new ApiError('Validation failed', 400, messages);
}
// If the error is not an operational error (e.g., programming error),
// send a generic 500 message to avoid leaking sensitive info.
if (!error.isOperational) {
error.statusCode = 500;
error.message = 'Something went very wrong!';
}
res.status(error.statusCode || 500).json({
success: false,
status: error.status || 'error',
message: error.message || 'Server Error',
errors: error.errors || []
});
};
module.exports = errorHandler;
Using in server.js:
// server.js
// ... (imports) ...
const ApiError = require('./utils/ApiError');
const errorHandler = require('./middleware/errorHandler');
// ... (connectDB, app.use(express.json()), routes) ...
// Example route using custom error
app.get('/api/books-fail/:id', async (req, res, next) => {
try {
const book = await Book.findById(req.params.id);
if (!book) {
// Pass the custom error to the error handling middleware
return next(new ApiError(`Book not found with ID ${req.params.id}`, 404));
}
res.status(200).json(book);
} catch (error) {
next(error); // Pass any other errors (e.g., CastError for invalid ID format)
}
});
// Catch-all for 404 Not Found (must be before the centralized error handler)
app.use((req, res, next) => {
res.status(404).json({
success: false,
message: `The resource at ${req.originalUrl} was not found.`
});
});
// Centralized Error Handling Middleware (MUST be the last middleware)
app.use(errorHandler);
// ... app.listen() ...
This pattern makes your API's error responses consistent and easier to debug.
Logging in Node.js Applications
Logging is essential for monitoring, debugging, and auditing your application in production.
-
Importance of logging:
- Debugging: Identify and fix issues.
- Monitoring: Track application health and performance.
- Auditing: Record important events (e.g., user logins, data changes).
- Security: Detect suspicious activities.
-
Request Logging with
morgan:morganis a popular HTTP request logger middleware for Node.js.npm install morgan// server.js const morgan = require('morgan'); // ... if (process.env.NODE_ENV === 'development') { app.use(morgan('dev')); // 'dev' format is concise, color-coded for development } // For production, you might use 'combined' or 'common' and pipe to a file // app.use(morgan('combined', { stream: accessLogStream })); // ... -
Application Logging with
WinstonorPino:For general application logging (errors, info, debug messages), dedicated logging libraries are preferred over
console.log(). Winston is a highly flexible and popular choice.npm install winston// config/logger.js const { createLogger, format, transports } = require('winston'); const { combine, timestamp, printf, colorize, align } = format; const logFormat = printf(({ level, message, timestamp, stack }) => { return `${timestamp} ${level}: ${stack || message}`; }); const logger = createLogger({ level: process.env.NODE_ENV === 'development' ? 'debug' : 'info', // Log level based on environment format: combine( timestamp({ format: 'YYYY-MM-DD HH:mm:ss' }), logFormat ), transports: [ new transports.Console({ format: combine( colorize(), align(), logFormat ) }), new transports.File({ filename: 'logs/error.log', level: 'error' }), new transports.File({ filename: 'logs/combined.log' }) ], exceptionHandlers: [ new transports.File({ filename: 'logs/exceptions.log' }) ] }); module.exports = logger;// server.js // ... const logger = require('./config/logger'); // Import your logger // ... // In your routes or middleware: app.post('/api/books', async (req, res, next) => { try { // ... logger.info('New book created:', newBook); res.status(201).json(newBook); } catch (error) { logger.error('Error creating book:', error); // Log the error next(error); } }); // For uncaught exceptions and unhandled promise rejections process.on('uncaughtException', (err) => { logger.error('Uncaught Exception:', err); process.exit(1); // Exit process }); process.on('unhandledRejection', (reason, promise) => { logger.error('Unhandled Rejection at:', promise, 'reason:', reason); // Optionally, exit process or handle gracefully });
Introduction to API Documentation
API documentation is crucial for developers (both frontend and other backend teams) to understand how to use your API.
-
Why document APIs?
- Improves developer experience.
- Ensures consistency.
- Facilitates maintenance and onboarding.
-
OpenAPI (Swagger) Specification:
A language-agnostic, machine-readable specification for describing RESTful APIs. It allows both humans and computers to understand the capabilities of a service without access to source code.
It defines paths, operations, parameters, request/response schemas, security schemes, etc.
-
Swagger UI:
A tool that automatically generates interactive API documentation from an OpenAPI specification. It provides a user-friendly web interface where users can explore endpoints, see request/response examples, and even make live API calls.
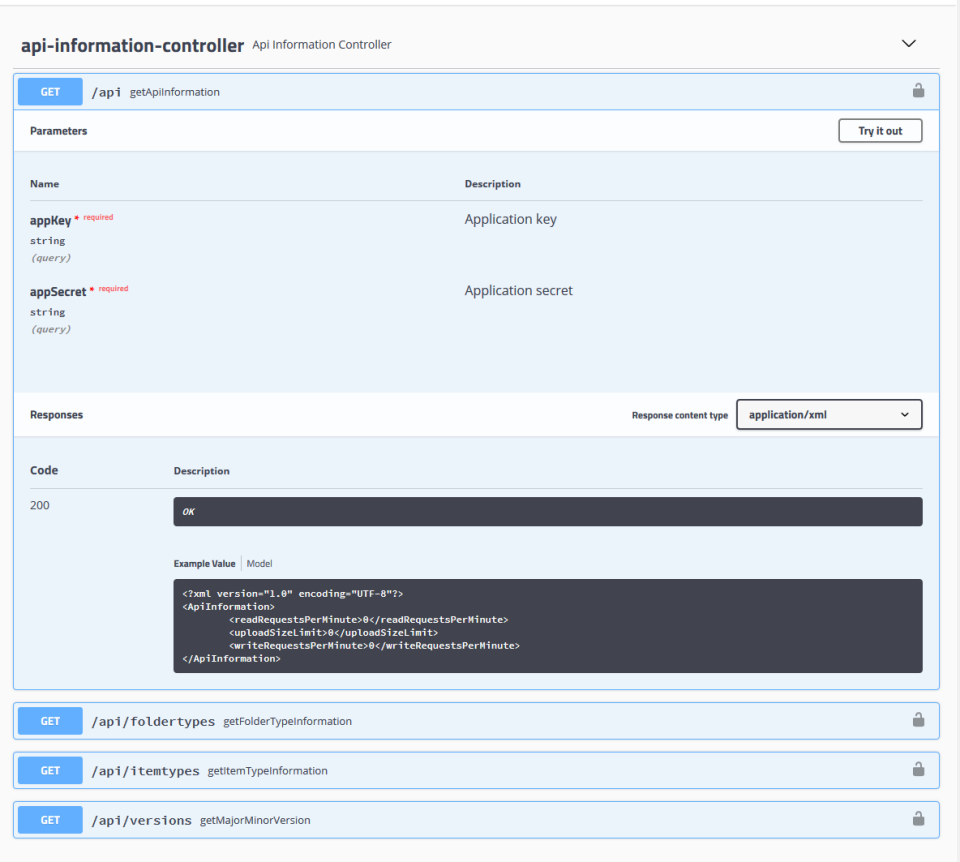
-
Generating documentation:
You can write OpenAPI specs manually (YAML or JSON) or use libraries that generate them from JSDoc comments in your code (e.g.,
swagger-jsdoc,express-swagger-generator).
Environment Configuration (Beyond .env)
While .env files are great for local development,
you'll need more robust solutions for managing configurations
across different environments (development, testing,
production).
-
Using different configurations:
You might have different database credentials, API keys, or logging levels for each environment.
// config/config.js module.exports = { development: { db: { uri: process.env.DEV_DB_URI }, jwtSecret: process.env.DEV_JWT_SECRET, logLevel: 'debug' }, production: { db: { uri: process.env.PROD_DB_URI }, jwtSecret: process.env.PROD_JWT_SECRET, logLevel: 'info' } }; // In server.js: // const config = require('./config/config')[process.env.NODE_ENV || 'development']; // console.log(config.db.uri); -
Managing sensitive data outside of code:
In production, environment variables are typically set directly on the hosting platform (e.g., Heroku config vars, AWS Lambda environment variables, Docker secrets) rather than using a
.envfile.
Mastering error handling, logging, and proper configuration is what separates a good backend developer from a great one. These practices ensure your applications are robust, maintainable, and observable in production. In the next section, we'll shift to deployment and other key topics.
