Class 23: RESTful API Principles
As we move into building more complex backend applications, especially those that serve data to frontend frameworks like React, understanding how to design effective APIs becomes crucial. Today, we'll delve into RESTful API principles, a widely adopted architectural style for designing networked applications.
Introduction to APIs (Application Programming Interfaces)
An API (Application Programming Interface) is a set of definitions and protocols for building and integrating application software. In simpler terms, it's a way for different software systems to communicate with each other.
- How different systems communicate: Imagine you're in a restaurant. You (the client) want food (a service). You don't go into the kitchen and cook it yourself. Instead, you interact with a waiter (the API). You tell the waiter what you want (make a request), and the waiter communicates with the kitchen (the server) to get your order prepared. Finally, the waiter brings you your food (the response).
- Web APIs: In web development, APIs typically involve communication over HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol). Your frontend (React app) will make HTTP requests to your backend API, and the backend will respond with data, usually in JSON format.
- Types of APIs: Some popular APIs are REST (Representational State Transfer), SOAP (Simple Object Access Protocol), and GraphQL.
What is REST? (Representational State Transfer)
REST is an architectural style, not a protocol or a standard. It provides a set of guidelines for building scalable, maintainable, and reliable web services. It was introduced by Roy Fielding in his 2000 doctoral dissertation.
A system that adheres to REST principles is called RESTful.
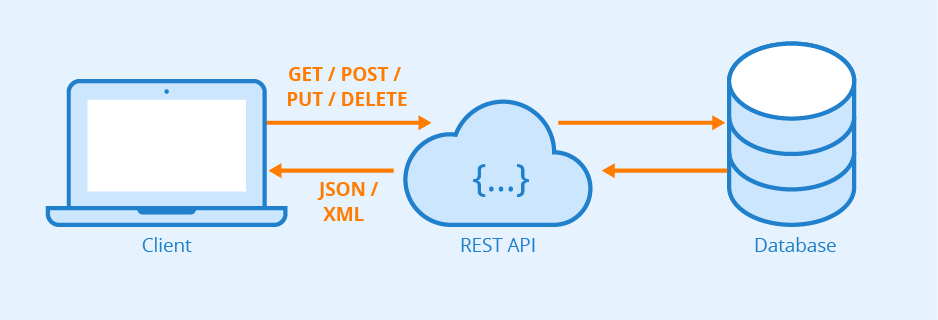
Key REST Principles (Constraints)
Roy Fielding defined six guiding constraints for RESTful systems:
-
Client-Server:
The client and server should be separate and independent of each other. This separation of concerns improves portability of the client UI across multiple platforms, and scalability of the server components.
-
Statelessness:
Each request from client to server must contain all the information needed to understand the request. The server should not store any client context between requests. This makes the API more scalable and reliable, as any server can handle any request.
-
Cacheable:
Responses must explicitly or implicitly define themselves as cacheable or non-cacheable. This allows clients to cache responses, improving performance and scalability by reducing server load.
-
Uniform Interface:
This is the most crucial constraint. It simplifies the overall system architecture and improves visibility of interactions. It includes four sub-constraints:
-
Resource-Based Identification (URIs):
Individual resources are identified in requests,
e.g., by URIs (Uniform Resource Identifiers).
Example:/users,/products/123 -
Manipulation of Resources Through
Representations:
Clients manipulate resources using representations
(e.g., JSON or XML) that are sent in the request
body.
Example: Sending a JSON object to create a new user. - Self-descriptive Messages: Each message includes enough information to describe how to process the message. This means the client doesn't need prior knowledge of the server's state. HTTP headers and status codes play a big role here.
- HATEOAS (Hypermedia as the Engine of Application State): This constraint suggests that responses should include links to related resources, guiding the client on what actions it can take next. While a core REST principle, it's often the least implemented in "RESTful" APIs.
-
Resource-Based Identification (URIs):
Individual resources are identified in requests,
e.g., by URIs (Uniform Resource Identifiers).
-
Layered System:
A client cannot ordinarily tell whether it is connected directly to the end server, or to an intermediary along the way. This allows for intermediate servers (e.g., load balancers, proxies, caches) to be added or removed without affecting the client or the end server.
-
Code on Demand (Optional):
Servers can temporarily extend or customize client functionality by transferring executable code (e.g., JavaScript applets). This constraint is optional and less commonly seen in typical REST APIs.
HTTP Methods and Their Semantics
RESTful APIs leverage standard HTTP methods to perform operations on resources. Each method has specific semantics:
-
GET: Retrieve resources.- Safe: Does not change the state of the server.
- Idempotent: Making the same GET request multiple times will yield the same result.
-
Example:
GET /api/products(get all products),GET /api/products/123(get product with ID 123).
-
POST: Create new resources.- Not Idempotent: Making the same POST request multiple times might create duplicate resources.
-
Example:
POST /api/products(create a new product).
-
PUT: Fully update/replace resources.- Idempotent: Sending the same PUT request multiple times will result in the same resource state. If the resource doesn't exist, PUT might create it (upsert).
-
Example:
PUT /api/products/123(replace product 123 with new data).
-
PATCH: Partially update resources.- Not Idempotent: Applying the same PATCH request multiple times might yield different results if not carefully designed.
-
Example:
PATCH /api/products/123(update only the price of product 123).
-
DELETE: Remove resources.- Idempotent: Deleting a resource multiple times will have the same effect (the resource remains deleted).
-
Example:
DELETE /api/products/123(delete product with ID 123).
Resource Naming Conventions (URIs)
A key aspect of REST is using clear, consistent, and predictable URIs (Uniform Resource Identifiers) to identify resources.
-
Use plural nouns for collections:
/products // Collection of products /users // Collection of users /orders // Collection of orders -
Use identifiers for specific resources:
/products/123 // Specific product with ID 123 /users/john_doe // Specific user with username 'john_doe' -
Avoid verbs in URIs:
The HTTP method (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE) already indicates the action. URIs should represent the resource.
// Bad examples: /getAllProducts /createNewUser /deleteProduct/456 // Good examples: GET /products POST /users DELETE /products/456 -
Nesting for relationships:
If a resource is conceptually a sub-resource of another, you can nest them.
/users/123/orders // All orders for user 123 /users/123/orders/abc // Specific order 'abc' for user 123
HTTP Status Codes
HTTP status codes are crucial for indicating the outcome of an API request. They provide immediate feedback to the client about whether the request was successful, failed, or requires further action.
- 1xx: Informational (e.g., 100 Continue)
-
2xx: Success
-
200 OK: The request was successful. (Common for GET, PUT, PATCH, DELETE) -
201 Created: The request has been fulfilled and resulted in a new resource being created. (Common for POST) -
204 No Content: The server successfully processed the request, but is not returning any content. (Common for DELETE when no body is needed)
-
- 3xx: Redirection (e.g., 301 Moved Permanently)
-
4xx: Client Error (The client made a bad
request)
-
400 Bad Request: The server cannot or will not process the request due to something that is perceived to be a client error (e.g., malformed request syntax, invalid request message framing, or deceptive request routing). -
401 Unauthorized: Authentication is required and has failed or has not yet been provided. -
403 Forbidden: The server understood the request but refuses to authorize it. (e.g., user doesn't have permission). -
404 Not Found: The requested resource could not be found on the server. -
405 Method Not Allowed: The HTTP method used is not allowed for the requested resource. -
409 Conflict: Indicates a request conflict with the current state of the target resource. (e.g., trying to create a resource that already exists with a unique ID).
-
-
5xx: Server Error (The server failed to
fulfill an apparently valid request)
-
500 Internal Server Error: A generic error message, given when an unexpected condition was encountered and no more specific message is suitable. -
503 Service Unavailable: The server is currently unable to handle the request due to a temporary overload or scheduled maintenance.
-
Request and Response Formats
While REST does not mandate a specific format, JSON (JavaScript Object Notation) has become the de-facto standard for data exchange in RESTful APIs due to its lightweight nature and ease of parsing in JavaScript.
-
Commonly JSON:
// Example Request Body (POST /api/products) { "name": "Laptop", "price": 1200, "description": "Powerful laptop for development" } // Example Response Body (GET /api/products/123) { "id": "123", "name": "Laptop", "price": 1200, "description": "Powerful laptop for development", "createdAt": "2023-07-20T10:00:00Z" } -
Content-TypeandAcceptheaders:-
Content-Type: Indicates the media type of the resource in the request or response body. When sending JSON, you'd set this toapplication/json. -
Accept: Indicates the media types that are acceptable for the response. A client might sendAccept: application/jsonto indicate it prefers JSON responses.
-
Understanding these RESTful principles is crucial for designing APIs that are intuitive, scalable, and easy to consume by frontend applications. In the next classes, we'll start implementing these principles by building a CRUD API with Express.js.
